- Welcome to CableDataSheet, Cable and Wire Technical Consulting Service.
Recent posts
#51
A3 Problem solving method / What is the A3 Problem solving...
Last post by tacettin - April 02, 2023, 01:11:39 AMWhat is the A3 Problem solving method ?
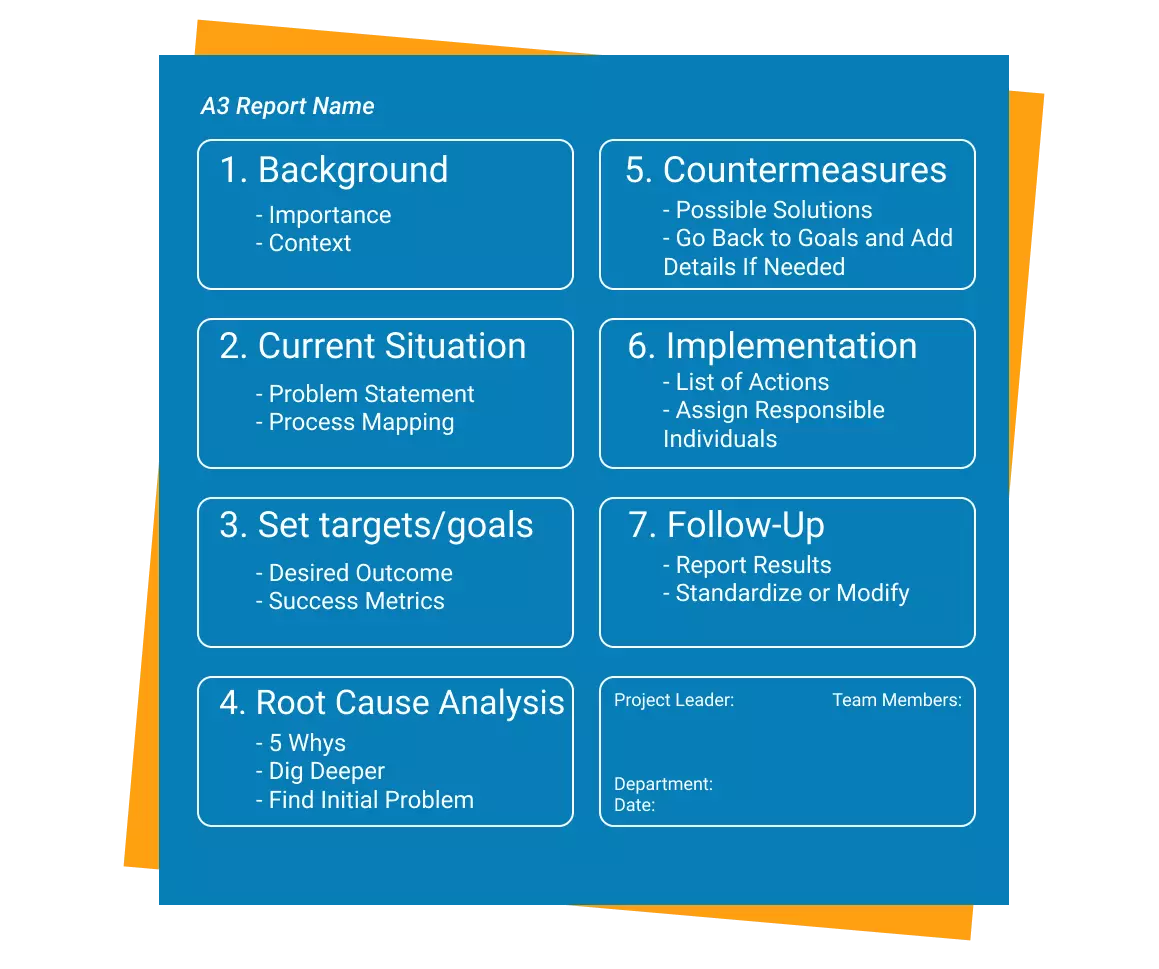
3 problem solving is a structured and collaborative approach to solving business problems. The A3 method takes its name from the size of paper (A3) typically used to document the process. The A3 problem-solving process typically consists of the following steps:
Identify the problem: Clearly define the problem and its impact on the business. This step includes understanding the gap between the current state and the desired future state.
Analyze the problem: Gather data and use root cause analysis tools to understand the cause and effect relationships of the problem. Use the data to develop a hypothesis of the root cause of the problem.
Develop countermeasures: Based on the analysis, develop potential countermeasures to address the root cause of the problem.
Implement countermeasures: Test the proposed solutions and implement the ones that are most effective.
Monitor results: Evaluate the results of the countermeasures and determine if they have effectively addressed the root cause of the problem.
Standardize the solution: Once a solution is found, establish standard work to ensure the solution is maintained and sustained.
The A3 problem-solving technique is a structured and collaborative approach that engages team members to share information and ideas, identify the root cause of the problem, and develop and implement effective solutions. The A3 approach is effective for solving complex problems and enables teams to make data-driven decisions that can lead to lasting improvements in business processes.
3 problem solving is a structured and collaborative approach to solving business problems. The A3 method takes its name from the size of paper (A3) typically used to document the process. The A3 problem-solving process typically consists of the following steps:
Identify the problem: Clearly define the problem and its impact on the business. This step includes understanding the gap between the current state and the desired future state.
Analyze the problem: Gather data and use root cause analysis tools to understand the cause and effect relationships of the problem. Use the data to develop a hypothesis of the root cause of the problem.
Develop countermeasures: Based on the analysis, develop potential countermeasures to address the root cause of the problem.
Implement countermeasures: Test the proposed solutions and implement the ones that are most effective.
Monitor results: Evaluate the results of the countermeasures and determine if they have effectively addressed the root cause of the problem.
Standardize the solution: Once a solution is found, establish standard work to ensure the solution is maintained and sustained.
The A3 problem-solving technique is a structured and collaborative approach that engages team members to share information and ideas, identify the root cause of the problem, and develop and implement effective solutions. The A3 approach is effective for solving complex problems and enables teams to make data-driven decisions that can lead to lasting improvements in business processes.

#52
DMAIC Problem solving method / What is the DMAIC Problem solv...
Last post by tacettin - April 02, 2023, 01:05:35 AMWhat is the DMAIC Problem solving method ?
DMAIC is a problem-solving technique that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a data-driven approach to problem-solving that aims to identify, measure, and eliminate problems in business processes. Here's an overview of the five steps in the DMAIC process:
Define: In this step, you define the problem, its scope, and its impact on the business. You also identify the customer needs and expectations related to the problem.
Measure: This step involves collecting data related to the problem and measuring the current performance of the process. You identify the critical process parameters and measure them to determine the baseline performance.
Analyze: In this step, you analyze the data collected in the previous step to determine the root cause of the problem. You use tools such as cause and effect diagrams, histograms, and statistical analysis to identify the underlying causes of the problem.
Improve: Based on the analysis of the data, you develop and implement solutions to address the root cause of the problem. You may need to test the solutions to ensure their effectiveness.
Control: In the final step, you establish controls to monitor the process and prevent the problem from recurring. You establish performance metrics, put monitoring systems in place, and train personnel to ensure that the improvements are sustained.
The DMAIC approach is commonly used in Six Sigma methodologies, but it can be applied in any business process that requires problem-solving. DMAIC is a systematic approach to problem-solving that helps businesses identify problems, analyze them, and develop solutions that are based on data and evidence.

DMAIC is a problem-solving technique that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a data-driven approach to problem-solving that aims to identify, measure, and eliminate problems in business processes. Here's an overview of the five steps in the DMAIC process:
Define: In this step, you define the problem, its scope, and its impact on the business. You also identify the customer needs and expectations related to the problem.
Measure: This step involves collecting data related to the problem and measuring the current performance of the process. You identify the critical process parameters and measure them to determine the baseline performance.
Analyze: In this step, you analyze the data collected in the previous step to determine the root cause of the problem. You use tools such as cause and effect diagrams, histograms, and statistical analysis to identify the underlying causes of the problem.
Improve: Based on the analysis of the data, you develop and implement solutions to address the root cause of the problem. You may need to test the solutions to ensure their effectiveness.
Control: In the final step, you establish controls to monitor the process and prevent the problem from recurring. You establish performance metrics, put monitoring systems in place, and train personnel to ensure that the improvements are sustained.
The DMAIC approach is commonly used in Six Sigma methodologies, but it can be applied in any business process that requires problem-solving. DMAIC is a systematic approach to problem-solving that helps businesses identify problems, analyze them, and develop solutions that are based on data and evidence.

#53
PDCA Problem solving method / What is the PDCA Problem solvi...
Last post by tacettin - April 02, 2023, 01:00:04 AMWhat is the PDCA Problem solving method ?
PDCA, also known as the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, is a cyclic problem-solving technique used to solve problems and improve business processes. Using this technique, you can identify problems, develop solutions, implement those solutions, and evaluate the results. The PDCA cycle consists of the following steps:
Planning: Firstly, you need to identify the problem, determine its causes, and develop solutions. In this step, you can set goals and measurable objectives.
Doing: This is the implementation stage where you put your plan into action.
Checking: To measure the effectiveness of your solutions, you need to evaluate the results. In this step, you check whether you have achieved your goals and what measurable outcomes have been achieved.
Acting: In the final step, you take actions to continually improve the process based on the results and data obtained.
The PDCA method is widely used to increase efficiency in businesses, organizations, and individuals. This method can be applied in various sectors and can help businesses solve problems related to quality control, production efficiency, customer satisfaction, and other business processes.

PDCA, also known as the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, is a cyclic problem-solving technique used to solve problems and improve business processes. Using this technique, you can identify problems, develop solutions, implement those solutions, and evaluate the results. The PDCA cycle consists of the following steps:
Planning: Firstly, you need to identify the problem, determine its causes, and develop solutions. In this step, you can set goals and measurable objectives.
Doing: This is the implementation stage where you put your plan into action.
Checking: To measure the effectiveness of your solutions, you need to evaluate the results. In this step, you check whether you have achieved your goals and what measurable outcomes have been achieved.
Acting: In the final step, you take actions to continually improve the process based on the results and data obtained.
The PDCA method is widely used to increase efficiency in businesses, organizations, and individuals. This method can be applied in various sectors and can help businesses solve problems related to quality control, production efficiency, customer satisfaction, and other business processes.

#54
FAQ About Cable / Re: What’s The Difference Betw...
Last post by tacettin - March 25, 2023, 09:16:30 AMPolyether Urethane vs. Polyester Urethane
When it comes to polyurethane, there are two main types: polyether urethane and polyester urethane. Although they are both polyurethanes, each has its own unique set of physical properties that are designed for specific applications. Below is a comparison of polyether and polyester polyurethanes showing lists of properties as well as applications for each material.
Polyester Urethane
In fact, polyesters are typically famous for their superior sliding abrasion resistance. Moreover, one should make an effort your current fortune bestes live caribbean stud poker casino. This makes them excellent for applications where abrasion subjects the polyurethane surface to high levels of friction, such as with chute liners and scraper blades. Typically, this is the main defining attribute when comparing polyesters with other materials. Polyesters are often called the "workhorse" of high abrasion applications and have gained an excellent reputation when used in highly abrasive environments.
Properties:
Excellent Abrasion Resistance
Better Shock Absorption
Higher Tensile Strength
Good Chemical Resistance
Withstand Higher Temperatures Longer
Applications:
Scraper blades
Chute liners
Hopper liners
Wear pads
Snowplow blades
Screening grids
Polyether Urethane
In fact, polyethers are the most common polyurethanes used in the cast elastomer industry. They generally have better dynamic properties than polyesters and are used in wide range of applications such as rollers, bumpers, and bushings. Polyethers tend to make up the majority of polyurethane parts because they are easy to work with and offer more desirable physical properties. Another very interesting thing about polyethers is that they can be tailored with specific additives to perform on the same level or better as polyesters for abrasion resistance. This results in a material that is essentially a hybrid polyether and performs just like a polyester in high scraping abrasion applications.
Properties:
Excellent Dynamic Properties
Hydrolytic Stability
Low-Temperature Flexibility
Good High-Temperature Resistance
UV Resistance
Better Rebound
Applications:
Rollers
High load casters
Skateboard wheels
Body Blocks
Bumpers
Bushings
Coil storage pads
Gears and sprockets
Pulleys
Couplings
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login
When it comes to polyurethane, there are two main types: polyether urethane and polyester urethane. Although they are both polyurethanes, each has its own unique set of physical properties that are designed for specific applications. Below is a comparison of polyether and polyester polyurethanes showing lists of properties as well as applications for each material.
Polyester Urethane
In fact, polyesters are typically famous for their superior sliding abrasion resistance. Moreover, one should make an effort your current fortune bestes live caribbean stud poker casino. This makes them excellent for applications where abrasion subjects the polyurethane surface to high levels of friction, such as with chute liners and scraper blades. Typically, this is the main defining attribute when comparing polyesters with other materials. Polyesters are often called the "workhorse" of high abrasion applications and have gained an excellent reputation when used in highly abrasive environments.
Properties:
Excellent Abrasion Resistance
Better Shock Absorption
Higher Tensile Strength
Good Chemical Resistance
Withstand Higher Temperatures Longer
Applications:
Scraper blades
Chute liners
Hopper liners
Wear pads
Snowplow blades
Screening grids
Polyether Urethane
In fact, polyethers are the most common polyurethanes used in the cast elastomer industry. They generally have better dynamic properties than polyesters and are used in wide range of applications such as rollers, bumpers, and bushings. Polyethers tend to make up the majority of polyurethane parts because they are easy to work with and offer more desirable physical properties. Another very interesting thing about polyethers is that they can be tailored with specific additives to perform on the same level or better as polyesters for abrasion resistance. This results in a material that is essentially a hybrid polyether and performs just like a polyester in high scraping abrasion applications.
Properties:
Excellent Dynamic Properties
Hydrolytic Stability
Low-Temperature Flexibility
Good High-Temperature Resistance
UV Resistance
Better Rebound
Applications:
Rollers
High load casters
Skateboard wheels
Body Blocks
Bumpers
Bushings
Coil storage pads
Gears and sprockets
Pulleys
Couplings
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login
#55
FAQ About Cable / Typical Elastomer Characterist...
Last post by tacettin - March 25, 2023, 09:05:16 AMTypical Elastomer Characteristics


#56
FAQ About Cable / What’s The Difference Between ...
Last post by tacettin - March 25, 2023, 09:02:10 AMWhat's The Difference Between Polyester based PU with Polyether based ?
Polyester based
Oil/solvent resistance
Resistance to weak acids/basics
Abrasion resistance
Excellent mechanical properties
Fungus Resistance
Excellent Vibratory Dampening
Polyester polyurethane is not recommended for use where high humidity or water exposure is a concern. Hydrolysis is a risk which will have a negative effect on the physical properties of the polyurethane.
Polyether based
Low-temperature flexibility
Excellent hydrolytic stability
Food Grade Applications
Temperature resistance
Excellent mechanical properties
Weather (UV) resistance
Polyether polyurethanes are recommended for applications which are expected to experience medium to high stress.
Abrasion Resistance Properties
Without question, the urethanes have outstanding abrasion resistance. They outwear metals, plastics, and other rubbers by a wide margin — often by 8 to 1 or more. Abrasion results from many actions, such as impingement, erosion, impact, scuffing, and sliding.
Sliding refers to scraping and rubbing abrasion. Impingement refers to particles or objects striking the urethane surface at a high angle.
Polyester polyurethane exhibits superior sliding abrasion resistance. This makes it it better suited for applications like scraper blades.
Heat Resistance Properties
Polyurethane elastomers can withstand continuous use up to 194°F (90°C). Flame retardants may be added to the formulation, if required. Both polyester and polyether urethanes perform well at high temperatures. But polyesters are better able to withstand high temperatures longer and are more resistant to heat aging.
Polyethers are less susceptible to dynamic heat build-up.
Low-temperature flexibility
Polyurethane elastomers get harder as temperatures drop. This makes them less flexible and potentially brittle. Depending on the formulation, the brittle point may be between -40°F and -100°F (-40°C and -73°C). Of the two polyurethane types, polyether polyurethane is less affected by cold temperatures.
Polyurethanes can withstand sudden and dramatic temperature drops without cracking. And even at their highest hardness levels, polyurethanes have a better impact resistance than most plastics.
Rebound properties
Some products need to return the energy they absorb (rebound). Polyether polyurethane provides higher rebound than polyester polyurethane.
Shock absorption properties
Sometimes you want the product to absorb the energy it receives (opposite of rebound). In this case, polyester urethane is the better option (e.g. vibration dampening applications).
Hardness Properties
Both polyester polyurethane and polyether polyurethane can be made to any hardness from soft to hard.
Cut and tear resistance
While both polyether and polyester polyurethanes are strong, polyester polyurethanes have a higher tensile strength and a higher cut and tear resistance than polyether polyurethanes.
Water and moisture resistance
Polyether polyurethanes should be selected if the product is to be placed under water or exposed to high humidity as they exhibit excellent hydrolytic stability.
Polyether polyurethanes can be stable in water as warm as 122°F (50°C) for long periods of time. However, they are not recommended for continuous use in water over 158°F (70°C). You can expect .3% to 1% increase in weight due to water absorption and there is a negligible swell in volume.
Polyester polyurethanes are not recommended for applications where water and high humidity is a concern.
Oil and chemical resistance
Polyester polyurethanes are more resistant to exposure to oils, fuels, or chemicals.
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login
Polyester based
Oil/solvent resistance
Resistance to weak acids/basics
Abrasion resistance
Excellent mechanical properties
Fungus Resistance
Excellent Vibratory Dampening
Polyester polyurethane is not recommended for use where high humidity or water exposure is a concern. Hydrolysis is a risk which will have a negative effect on the physical properties of the polyurethane.
Polyether based
Low-temperature flexibility
Excellent hydrolytic stability
Food Grade Applications
Temperature resistance
Excellent mechanical properties
Weather (UV) resistance
Polyether polyurethanes are recommended for applications which are expected to experience medium to high stress.
Abrasion Resistance Properties
Without question, the urethanes have outstanding abrasion resistance. They outwear metals, plastics, and other rubbers by a wide margin — often by 8 to 1 or more. Abrasion results from many actions, such as impingement, erosion, impact, scuffing, and sliding.
Sliding refers to scraping and rubbing abrasion. Impingement refers to particles or objects striking the urethane surface at a high angle.
Polyester polyurethane exhibits superior sliding abrasion resistance. This makes it it better suited for applications like scraper blades.
Heat Resistance Properties
Polyurethane elastomers can withstand continuous use up to 194°F (90°C). Flame retardants may be added to the formulation, if required. Both polyester and polyether urethanes perform well at high temperatures. But polyesters are better able to withstand high temperatures longer and are more resistant to heat aging.
Polyethers are less susceptible to dynamic heat build-up.
Low-temperature flexibility
Polyurethane elastomers get harder as temperatures drop. This makes them less flexible and potentially brittle. Depending on the formulation, the brittle point may be between -40°F and -100°F (-40°C and -73°C). Of the two polyurethane types, polyether polyurethane is less affected by cold temperatures.
Polyurethanes can withstand sudden and dramatic temperature drops without cracking. And even at their highest hardness levels, polyurethanes have a better impact resistance than most plastics.
Rebound properties
Some products need to return the energy they absorb (rebound). Polyether polyurethane provides higher rebound than polyester polyurethane.
Shock absorption properties
Sometimes you want the product to absorb the energy it receives (opposite of rebound). In this case, polyester urethane is the better option (e.g. vibration dampening applications).
Hardness Properties
Both polyester polyurethane and polyether polyurethane can be made to any hardness from soft to hard.
Cut and tear resistance
While both polyether and polyester polyurethanes are strong, polyester polyurethanes have a higher tensile strength and a higher cut and tear resistance than polyether polyurethanes.
Water and moisture resistance
Polyether polyurethanes should be selected if the product is to be placed under water or exposed to high humidity as they exhibit excellent hydrolytic stability.
Polyether polyurethanes can be stable in water as warm as 122°F (50°C) for long periods of time. However, they are not recommended for continuous use in water over 158°F (70°C). You can expect .3% to 1% increase in weight due to water absorption and there is a negligible swell in volume.
Polyester polyurethanes are not recommended for applications where water and high humidity is a concern.
Oil and chemical resistance
Polyester polyurethanes are more resistant to exposure to oils, fuels, or chemicals.
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login
#57
FAQ About Cable / Re: What are the difference be...
Last post by tacettin - March 18, 2023, 12:32:27 PM #58
FAQ About Cable / Re: What are the difference be...
Last post by tacettin - March 13, 2023, 11:31:29 AM #59
FAQ About Cable / Re: What are the difference be...
Last post by tacettin - March 13, 2023, 11:25:13 AM #60
FAQ About Cable / Re: What are the difference be...
Last post by tacettin - March 13, 2023, 09:36:42 AMAre you looking for an intrinsic safety barrier for your IS product?
Intrinsic safety is a system concept, and it is necessary to consider the safety of each component of the system in the loop.
An Intrinsic safety system involves three main components:
An intrinsically safe field device
A safety barrier, the energy limiting device
Intrinsically safe field wiring which connects the barrier to the field device
The challenge is to correctly select and match the safety barrier with the IS device located in a hazardous area for a safe connection.
The answer involves using the entity concept.
"Entity concept" is a globally recognized method that specifies the maximum energy a given safety barrier can ever deliver. The same method specifies the maximum energy a given field device can ever receive and still be safe.
In this way, the Entity Concept allows for the interconnection of intrinsically safe field devices with safety barriers that are not specifically tested in combination.
The entity concept is based on what are called "entity parameters" - allowable values on which approval was based.
For the intrinsically safe field device, the entity parameters relate to the maximum allowable amount of voltage, current and power which may be received as an input, as well as the maximum allowable equivalent internal capacitance and inductance.
The entity parameters of an IS field device are:
Ui the highest acceptable input voltage
Ii the highest acceptable input current
Pi the highest acceptable input power
Ci the maximum equivalent internal capacitance
Li the maximum equivalent internal inductance
For the safety barrier, the maximum allowable the entity parameters are the maximum amount of voltage, current and power the safety barrier can deliver to a hazardous area, as well as the maximum permitted capacitance and inductance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier. The entity parameters for a safety barrier are listed on its certificate, as well as on its nameplate and installation drawing.
The entity parameters of a safety barrier are:
Uo the maximum voltage a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area in the case of a fault
Io the maximum current a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area in a fault situation
Po the maximum power a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area
Co the maximum permitted capacitance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier
Lo The maximum permitted inductance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier
In order to have an accurate and safe connection between the safety barrier and the IS field device, the input voltage of the IS field device must be greater than or equal to the output voltage of the safety barrier. (Uo ≤ Ui)
The same relationship is true for current and power. (Io ≤ Ii and Po ≤ Pi )
The maximum equivalent internal capacitance of the intrinsically safe device must be less than or equal to the maximum allowed capacitance of the connected safety barrier (Co ≥ Ci). The same is true of the inductance value (Lo ≥ Li).
Because the field wiring cables have capacitance and inductance values, these values must also be taken into account. The total capacitance of the intrinsic safety system is therefore the capacitance of the field device PLUS the capacitance of the cables. This total must be less than or equal to the maximum permitted value of the safety barrier. The same is true for inductance. (Co ≥ Ci + Ccable and Lo ≥ Li + Lcable )
Summary:
Uo ≤ Ui
Io ≤ Ii
Po ≤ Pi
Co ≥ Ci + Ccable
Lo ≥ Li + Lcable

We have created an easy-to-use Intrinsic Safety Wiki to help you find the safety barrier that is safe to provide energy for your intrinsically safe device. Simply fill in the following fields and input the entity parameters of your IS device. Please note that all the fields must be filled. Pay attention to the units for each field. You can also add the maximum length in meters of the connection cable and our IS Wiki will calculate it into the equations. We consider that cables have 200pF/m capacitance value and 1µH/m inductance value.
Notes:
1. You need to check the compatibility of the selected safety barrier with your IS field device regarding the gas group/ dust groups and the equipment protection level (EPL).
2. For installations in which both the Ci and Li of the intrinsically safe apparatus exceed 1% of the Co and Lo parameters of the associated apparatus (excluding the cable), only 50% of Co and Lo parameters are applicable and shall not be exceeded.
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login
Intrinsic safety is a system concept, and it is necessary to consider the safety of each component of the system in the loop.
An Intrinsic safety system involves three main components:
An intrinsically safe field device
A safety barrier, the energy limiting device
Intrinsically safe field wiring which connects the barrier to the field device
The challenge is to correctly select and match the safety barrier with the IS device located in a hazardous area for a safe connection.
The answer involves using the entity concept.
"Entity concept" is a globally recognized method that specifies the maximum energy a given safety barrier can ever deliver. The same method specifies the maximum energy a given field device can ever receive and still be safe.
In this way, the Entity Concept allows for the interconnection of intrinsically safe field devices with safety barriers that are not specifically tested in combination.
The entity concept is based on what are called "entity parameters" - allowable values on which approval was based.
For the intrinsically safe field device, the entity parameters relate to the maximum allowable amount of voltage, current and power which may be received as an input, as well as the maximum allowable equivalent internal capacitance and inductance.
The entity parameters of an IS field device are:
Ui the highest acceptable input voltage
Ii the highest acceptable input current
Pi the highest acceptable input power
Ci the maximum equivalent internal capacitance
Li the maximum equivalent internal inductance
For the safety barrier, the maximum allowable the entity parameters are the maximum amount of voltage, current and power the safety barrier can deliver to a hazardous area, as well as the maximum permitted capacitance and inductance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier. The entity parameters for a safety barrier are listed on its certificate, as well as on its nameplate and installation drawing.
The entity parameters of a safety barrier are:
Uo the maximum voltage a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area in the case of a fault
Io the maximum current a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area in a fault situation
Po the maximum power a barrier can deliver to the hazardous area
Co the maximum permitted capacitance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier
Lo The maximum permitted inductance that may be safely connected to the output of the safety barrier
In order to have an accurate and safe connection between the safety barrier and the IS field device, the input voltage of the IS field device must be greater than or equal to the output voltage of the safety barrier. (Uo ≤ Ui)
The same relationship is true for current and power. (Io ≤ Ii and Po ≤ Pi )
The maximum equivalent internal capacitance of the intrinsically safe device must be less than or equal to the maximum allowed capacitance of the connected safety barrier (Co ≥ Ci). The same is true of the inductance value (Lo ≥ Li).
Because the field wiring cables have capacitance and inductance values, these values must also be taken into account. The total capacitance of the intrinsic safety system is therefore the capacitance of the field device PLUS the capacitance of the cables. This total must be less than or equal to the maximum permitted value of the safety barrier. The same is true for inductance. (Co ≥ Ci + Ccable and Lo ≥ Li + Lcable )
Summary:
Uo ≤ Ui
Io ≤ Ii
Po ≤ Pi
Co ≥ Ci + Ccable
Lo ≥ Li + Lcable

We have created an easy-to-use Intrinsic Safety Wiki to help you find the safety barrier that is safe to provide energy for your intrinsically safe device. Simply fill in the following fields and input the entity parameters of your IS device. Please note that all the fields must be filled. Pay attention to the units for each field. You can also add the maximum length in meters of the connection cable and our IS Wiki will calculate it into the equations. We consider that cables have 200pF/m capacitance value and 1µH/m inductance value.
Notes:
1. You need to check the compatibility of the selected safety barrier with your IS field device regarding the gas group/ dust groups and the equipment protection level (EPL).
2. For installations in which both the Ci and Li of the intrinsically safe apparatus exceed 1% of the Co and Lo parameters of the associated apparatus (excluding the cable), only 50% of Co and Lo parameters are applicable and shall not be exceeded.
source : You are not allowed to view links. Register or Login


